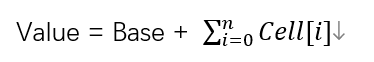JUC(六)-原子操作类及十八罗汉增强
本文最后更新于:2024年4月22日 下午
理解atomic原子类的基本类型原子类、数组类型原子类、引用类型原子类、对象的属性修改原子类的概要思想与案例分析
18罗汉=12原子类+4增强类+Striped64类+Number类
基本类型原子类
AtomicInteger
public final int get():获取当前的值
public final int getAndSet(int newValue):获取当前的值,并设置新的值
public final int getAndIncrement():获取当前的值,并自增(类似i++)
public final int incrementAndGet():自增后再获取当前的值(类似++i)
public final int getAndDecrement():获取当前的值,并自减
public final int getAndAdd(int delta):获取当前的值,并加上预期的值
void lazySet(int newValue): 最终会设置成newValue,使用lazySet设置值后,可能导致其他线程在之后的一小段时间内还是可以读到旧的值。package cn.hyqup.juc;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* Copyright © 2022 灼华. All rights reserved.
*
* @author create by hyq
* @version 0.1
* @date 2022/6/21
* @description:
*/
class MyNumber {
private AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger();
public void addPlusPlus() {
atomicInteger.incrementAndGet();
}
public AtomicInteger getAtomicInteger() {
return atomicInteger;
}
public void setAtomicInteger(AtomicInteger atomicInteger) {
this.atomicInteger = atomicInteger;
}
}
public class AtomicIntegerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyNumber myNumber = new MyNumber();
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(100);
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int j = 1; j <= 5000; j++) {
myNumber.addPlusPlus();
}
} finally {
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}, String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println(myNumber.getAtomicInteger().get());
}
}扩展知识CountDownLatch
它是一个同步工具类,允许一个或多个线程一直等待,直到其他线程运行完成后再执行。
使用场景:
场景1:让多个线程等待
多个线程awit()的时候,等待某个线程调用countDown来触发
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { new Thread(() -> { try { //准备完毕……运动员都阻塞在这,等待号令 countDownLatch.await(); String parter = "【" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "】"; System.out.println(parter + "开始执行……"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }).start(); } Thread.sleep(2000);// 裁判准备发令 countDownLatch.countDown();// 发令枪:执行发令场景2:和让单个线程等待
多线程执行任务的同时,主线程等待多线程执行完成后,再在主线程得到数据,上面的AtomicIntegerDemo就是这种场景
AtomicBoolean
原子更新布尔类型,用法类似
AtomicLong
原子更新长整型,用法类似
原子更新数组
AtomicIntegerArray
原子更新整型数组里的元素。
AtomicLongArray
原子更新长整型数组里的元素。
AtomicReferenceArray
原子更新引用类型数组里的元素。
引用类型原子类
上一章节讲到的ABA问题,这里就使用AtomicStampedReference和AtomicMarkableReference解决
AtomicReference
原子更新引用类型,通过CAS原理调用compareAndSet
AtomicStampedReference
原子更新引用类型, 内部使用Pair来存储元素值及其版本号,携带版本号的引用类型原子类,解决修改过几次
package cn.hyqup.juc;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicStampedReference;
/**
* Copyright © 2022 灼华. All rights reserved.
*
* @author create by hyq
* @version 0.1
* @date 2022/6/21
* @description:
*/
public class AtomicStampedReferenceDemo {
static AtomicStampedReference atomicStampedReference = new AtomicStampedReference(1, 0);
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("操作线程" + Thread.currentThread() + ",初始值 a = " + atomicStampedReference.getReference());
int stamp = atomicStampedReference.getStamp(); //获取当前标识别
try {
Thread.sleep(1000); //等待1秒 ,以便让干扰线程执行
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
boolean isCASSuccess = atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(1, 2, stamp, stamp + 1); //此时expectedReference未发生改变,但是stamp已经被修改了,所以CAS失败
System.out.println("操作线程" + Thread.currentThread() + ",CAS操作结果: " + isCASSuccess);
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
Thread.yield(); // 确保thread-main 优先执行
atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(1, 2, atomicStampedReference.getStamp(), atomicStampedReference.getStamp() + 1);
System.out.println("操作线程" + Thread.currentThread() + ",【increment】 ,值 = " + atomicStampedReference.getReference());
atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(2, 1, atomicStampedReference.getStamp(), atomicStampedReference.getStamp() + 1);
System.out.println("操作线程" + Thread.currentThread() + ",【decrement】 ,值 = " + atomicStampedReference.getReference());
}, "t2").start();
}
}AtomicMarkableReference
原子更新带有标记位的引用类型,原子更新带有标记位的引用类型对象,解决是否修改过
对象的属性修改原子类
以一种线程安全的方式操作非线程安全对象内的某些字段
使用要求(重点)
1、更新的对象属性必须使用 public volatile 修饰符
2、因为对象的属性修改类型原子类都是抽象类,所以每次使用都必须
使用静态方法newUpdater()创建一个更新器,并且需要设置想要更新的类和属性。
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater
package cn.hyqup.juc;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater;
/**
* Copyright © 2022 灼华. All rights reserved.
*
* @author create by hyq
* @version 0.1
* @date 2022/6/21
* @description:
*/
class BankAccount
{
private String bankName = "ZG";
public volatile int money = 0;
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<BankAccount> accountAtomicIntegerFieldUpdater = AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(BankAccount.class,"money");
//不加锁+性能高,局部微创
public void transferMoney(BankAccount bankAccount)
{
accountAtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.incrementAndGet(bankAccount);
}
}
public class AtomicIntegerFieldUpdaterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BankAccount bankAccount = new BankAccount();
for (int i = 1; i <=1000; i++) {
int finalI = i;
new Thread(() -> {
bankAccount.transferMoney(bankAccount);
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
//暂停毫秒
try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println(bankAccount.money);
}
}AtomicLongFieldUpdater
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater
package cn.hyqup.juc;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater;
/**
* Copyright © 2022 灼华. All rights reserved.
*
* @author create by hyq
* @version 0.1
* @date 2022/6/21
* @description:
*/
class MyVar
{
public volatile Boolean isInit = Boolean.FALSE;
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater<MyVar,Boolean> atomicReferenceFieldUpdater = AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater.newUpdater(MyVar.class,Boolean.class,"isInit");
public void init(MyVar myVar)
{
if(atomicReferenceFieldUpdater.compareAndSet(myVar,Boolean.FALSE,Boolean.TRUE))
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"---init.....");
//暂停几秒钟线程
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"---init.....over");
}else{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"------其它线程正在初始化");
}
}
}
public class AtomicReferenceFieldUpdaterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyVar myVar = new MyVar();
for (int i = 1; i <=5; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
myVar.init(myVar);
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}原子操作增强类
- DoubleAccumulator
- DoubleAdder
- LongAccumulator
- LongAdder
Adder和Accumulator区别:Adder只能用来计算加法,且从零开始计算;Accumulator提供了自定义的函数操作
package cn.hyqup.juc;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.LongAccumulator;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.LongAdder;
/**
* Copyright © 2022 灼华. All rights reserved.
*
* @author create by hyq
* @version 0.1
* @date 2022/6/22
* @description:
*/
public class LongAdderDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LongAdder longAdder = new LongAdder();
longAdder.increment();
longAdder.increment();
longAdder.increment();
System.out.println(longAdder.longValue());
LongAccumulator longAccumulator = new LongAccumulator((x, y) -> x * y, 2);
longAccumulator.accumulate(1);
longAccumulator.accumulate(2);
longAccumulator.accumulate(3);
System.out.println(longAccumulator.longValue());
}
}增强类(Adder、Accumulator)和Atomic的区别?
具体:LongAdder 与 AtomicLong有什么区别?
概述
AtomicLong是作者Doug Lea在jdk1.5版本发布于java.util.concurrent.atomic并发包下的类。
而LongAdder是道格·利(Doug Lea的中文名)在java8中发布的类。
原理剖析
AtomicLong底层是通过CAS实现的,采用volatile+Unsafe类来实现。
缺点:
1、在多线程竞争不激烈的情况下,这样做是合适的。但是如果线程竞争激烈,会造成大量线程在原地打转、不停尝试去修改值,但是老是发现值被修改了,于是继续自旋。 这样浪费了大量的CPU资源。
2、volatile,线程修改了临界资源后,需要刷新到其他线程,也会浪费资源
注意:Adder的实现sum求和后还有计算线程修改结果的话,最后结果不够准确
Striped64类
LongAdder是Striped64的子类
核心参数
Striped64有几个比较重要的成员函数
static final int NCPU = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
CPU数量,即cells数组的最大长度
transient volatile Cell[] cells;
cells数组,为2的幂,2,4,8,16…..,方便以后位运算
transient volatile long base;
基础value值,当并发较低时,只累加该值主要用于没有竞争的情况,通过CAS更新。
transient volatile int cellsBusy;
创建或者扩容Cells数组时使用的自旋锁变量调整单元格大小(扩容),创建单元格时使用的锁。
LongAdder实现原理:
LongAdder的基本思路就是分散热点,将value值分散到一个Cell数组中,不同线程会命中到数组的不同槽中,各个线程只对自己槽中的那个值进行CAS操作,这样热点就被分散了,冲突的概率就小很多。如果要获取真正的long值,只要将各个槽中的变量值累加返回。
sum()会将所有Cell数组中的value和base累加作为返回值,核心的思想就是将之前AtomicLong一个value的更新压力分散到多个value中去