剑指源码-spring(四)-后置处理器干预生命周期
本文最后更新于:2024年4月22日 下午
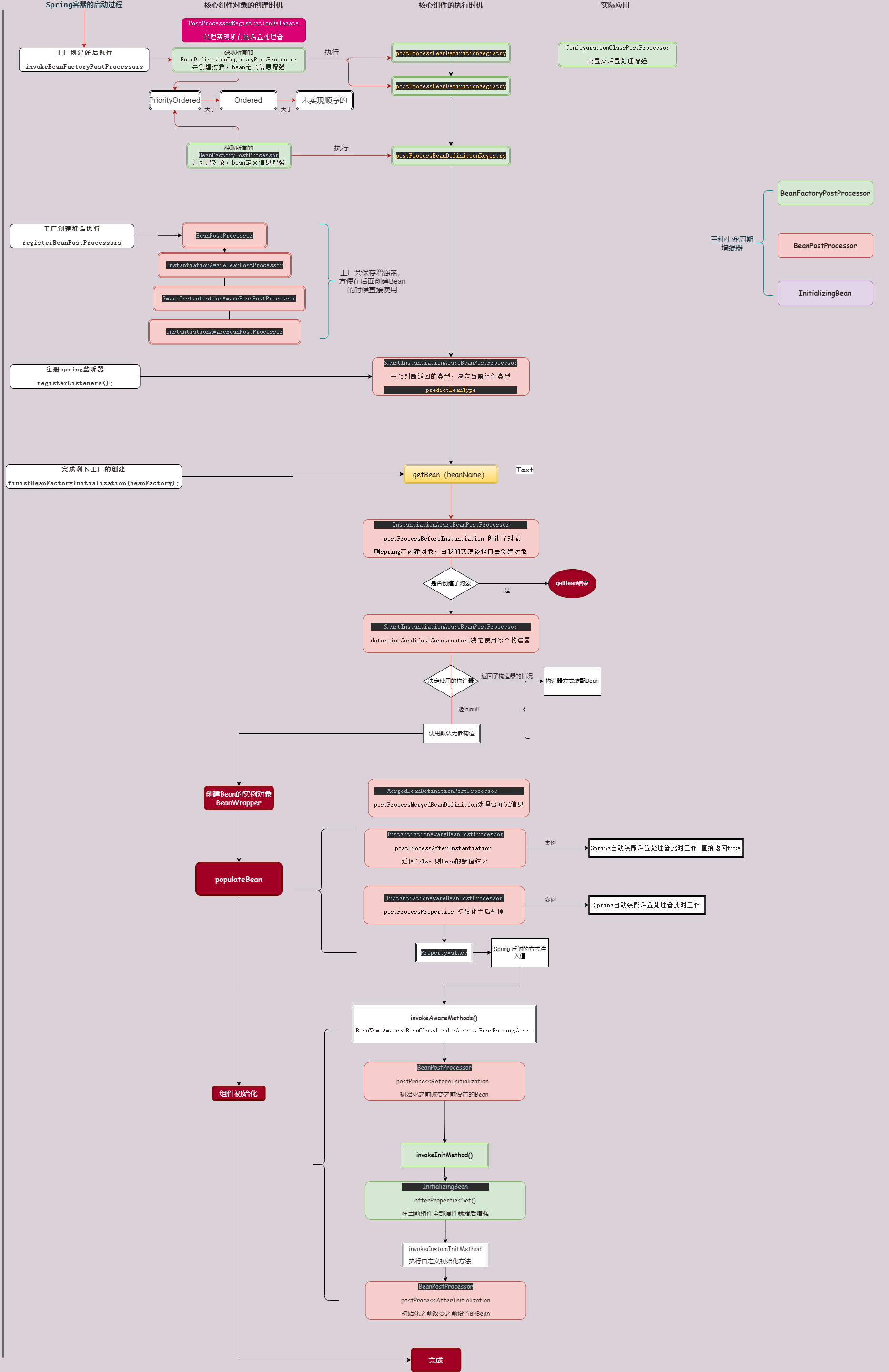
通过源码了解到整个生命周期中,有三种类型的 生命周期增强器 BeanFactoryPostProcessor(Bean工厂增强),BeanPostProcessor(Bean后置处理器)以及InitializingBean(初始化Bean增强),本章节分析这些增强器是如何干预生命周期的
前言
🎉BeanFactoryPostProcessor:后置增强工厂
🎨BeanPostProcessor: 后置增强组件,实现类很多,在于改变原有对象
✨InitializingBean: 组件初始化之后进行后续增强,与BeanPostProcessor不用的是,InitializingBean在于额外处理,因为这里不会传入当前对象的任何额外信息
实际工作面试中,考察对Spring的了解程度,其本质上是对多少种处理器了解
准备工作
我们这里去实现了许多的PostProcessor,依次打入断点还是源头打入断点调试堆栈信息
@Component
public class Cat {
public Cat() {
System.out.println("猫被创建了");
}
}
@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
public MyBeanPostProcessor() {
System.out.println("MyBeanPostProcessor 构造器执行.....");
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("执行 MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization .....................");
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("执行 MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization .....................");
return bean;
}
}
public class MyInitializingBean implements InitializingBean {
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("执行 MyInitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet .....................");
}
}
@Component
public class MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
public MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor() {
System.out.println("MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 构造器执行.....");
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("执行 MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInstantiation .....................");
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("执行 MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInstantiation .....................");
return true;
}
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("执行 MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessProperties .....................");
return null;
}
}
@Component
public class MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor implements MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor {
public MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor() {
System.out.println("MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 构造器执行.....");
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("执行 MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization .....................");
return null;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("执行 MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization .....................");
return null;
}
@Override
public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
System.out.println("执行 MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition .....................");
}
@Override
public void resetBeanDefinition(String beanName) {
System.out.println("执行 MyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor.resetBeanDefinition .....................");
}
}
@Component
public class MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor implements SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Class<?> predictBeanType(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("执行 MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.predictBeanType .....................");
return null;
}
@Override
public Constructor<?>[] determineCandidateConstructors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("执行 MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.determineCandidateConstructors .....................");
return new Constructor[0];
}
@Override
public Object getEarlyBeanReference(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("执行 MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.getEarlyBeanReference .....................");
return null;
}
}
@Component
public class MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("执行 MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor postProcessBeanFactory .....................");
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("执行 MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry .....................");
}
}
@Component
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("执行 MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessBeanFactory .....................");
}
}
使用 ComponentScan 来扫描注解@Componment
@ComponentScan("cn.hyqup.spring")
@Configuration
public class MainConfig {
}
public class AnnotationMainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
Cat bean = applicationContext.getBean(Cat.class);
System.out.println(bean);
}
}堆栈分析
类型一:BeanFactoryPostProcessor类型的工厂后置处理器
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 代码入口
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext refresh()
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
//告诉子类刷新内部 bean 工厂。
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 执行所有的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor,理由BeanFactory后置增强器对工厂进行修改或增强
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 完成Bean 工厂的初始化
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 为BeanFactoryPostProcessors核心入口方法,发生在BeanFactory创建之后
BeanFactoryPostProcessor注册
refresh() 中的 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 方法就是执行所有BeanFactory 后置增强器
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (!NativeDetector.inNativeImage() && beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
BeanFactoryPostProcessor执行
执行invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 核心逻辑
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// WARNING: Although it may appear that the body of this method can be easily
// refactored to avoid the use of multiple loops and multiple lists, the use
// of multiple lists and multiple passes over the names of processors is
// intentional. We must ensure that we honor the contracts for PriorityOrdered
// and Ordered processors. Specifically, we must NOT cause processors to be
// instantiated (via getBean() invocations) or registered in the ApplicationContext
// in the wrong order.
//
// Before submitting a pull request (PR) to change this method, please review the
// list of all declined PRs involving changes to PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate
// to ensure that your proposal does not result in a breaking change:
// https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/issues?q=PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate+is%3Aclosed+label%3A%22status%3A+declined%22
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
//首先,调用实现 PriorityOrdered 的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// 判断是否实现了顺序接口,数字越小,优先级越高
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
// 从容器中获取这个组件,并放到该集合,getBean 没有则会去创建
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
// 执行 当前接口的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}这里首先会判断 是否实现BeanDefinitionRegistry 接口。
里面分三种
1、实现 PriorityOrdered 顺序优先级最高
2、Ordered顺序,低于PriorityOrdered
3、普通未实现顺序接口
按照这样的顺序去调用 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors ,就是接口的根方法
顺序都是数字越小,优先级越高
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 中会循环调用相关接口的方法
实例分析
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
就是通过实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,扫描配置类及其相关注解,如@Componment @componmentScan 来将这些信息封装为BeanDefinition以供后续创建bean的定义信息
类型二:BeanPostProcessor类型为Bean的后置处理器增强
BeanPostProcessor的注册
refresh()方法中的registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory) 入口
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
// WARNING: Although it may appear that the body of this method can be easily
// refactored to avoid the use of multiple loops and multiple lists, the use
// of multiple lists and multiple passes over the names of processors is
// intentional. We must ensure that we honor the contracts for PriorityOrdered
// and Ordered processors. Specifically, we must NOT cause processors to be
// instantiated (via getBean() invocations) or registered in the ApplicationContext
// in the wrong order.
//
// Before submitting a pull request (PR) to change this method, please review the
// list of all declined PRs involving changes to PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate
// to ensure that your proposal does not result in a breaking change:
// https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/issues?q=PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate+is%3Aclosed+label%3A%22status%3A+declined%22
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));
// Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// 获取所有实现 PriorityOrdered
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
// 内部的
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
//首先,注册实现 PriorityOrdered 的 BeanPostProcessor。
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
// Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
// 接下来,注册实现 Ordered 的 BeanPostProcessor。
List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
// Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors.
// 现在,注册所有常规的 BeanPostProcessor。 getBean
List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
// Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
// Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners,
// moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc).
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext));
}流程如上,和BeanFactoryPostProcessor 大致逻辑类似整个流程完成注册
BeanPostProcessor执行
由于各种类型的BeanPostProcessor在Bean的生命周期干扰的时机不同,所以执行的时机也是不同的,这里我们会分别针对各个子类BeanPostProcessor接口代码分析干扰的时机
SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor
类型三:InitializingBean 完成bean 初始化后的操作
堆栈方法追踪:getBean->doGetBean->getSingleton->createBean->doCreateBean->initializeBean->invokeInitMethods
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
throw pae.getException();
}
}
else {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
}
}
if (mbd != null && bean.getClass() != NullBean.class) {
String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(initMethodName) &&
!(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&
!mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {
invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
}
}bean 完成之后会执行InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet